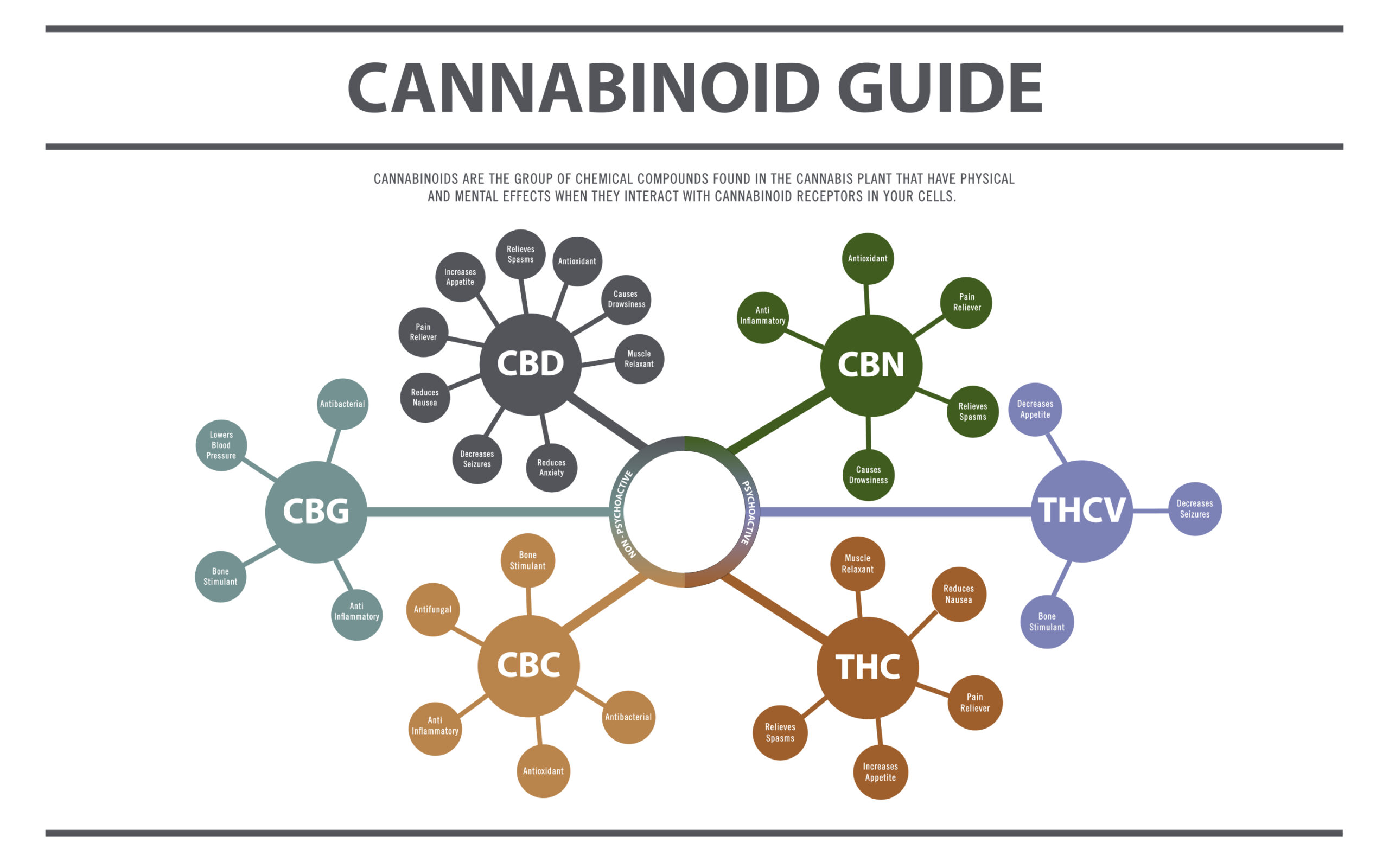
How does Cannabis work?

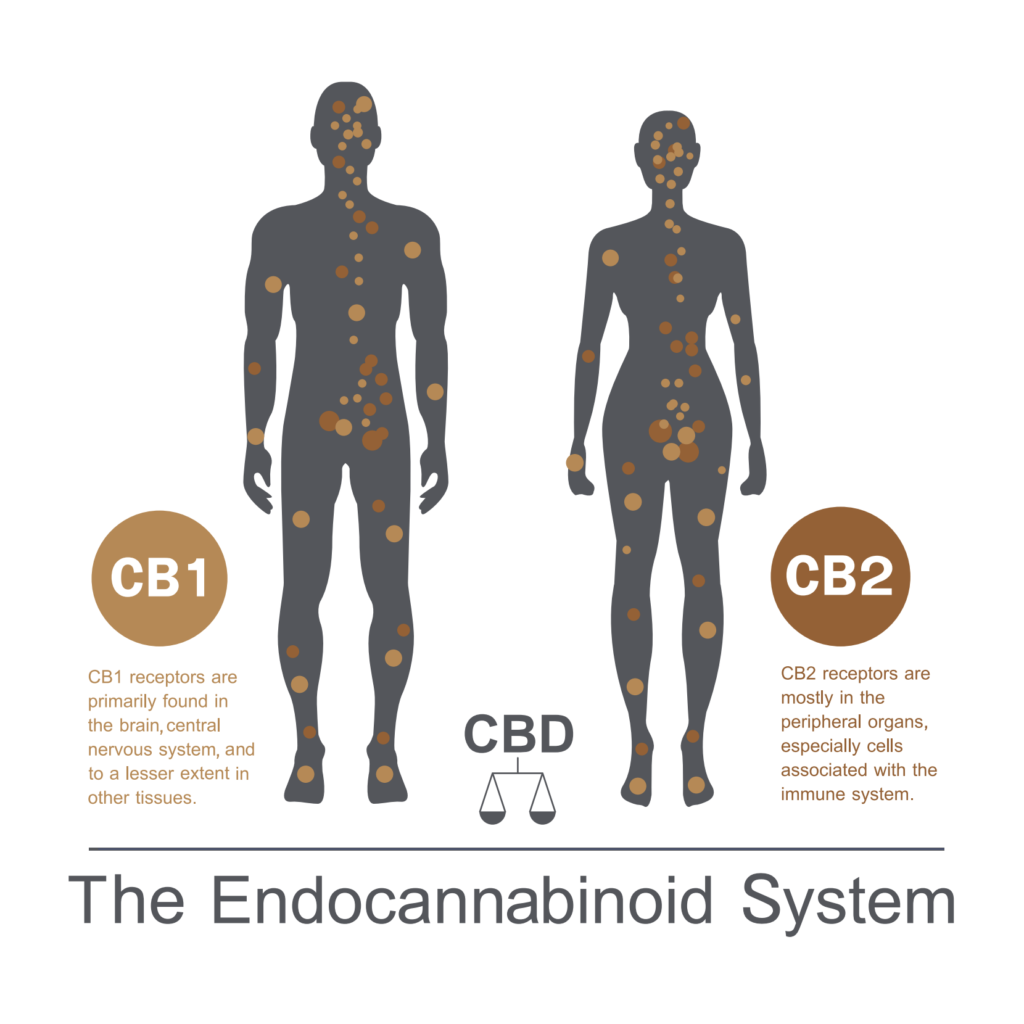
The human body is equipped with an endocannabinoid system (ECS), a series of cellular receptors that react to imbalances within the body and work to establish stability, or homeostasis. The system consists of two receptors, CB1 and CB2. CB1 receptors are primarily located in the brain, central nervous system, and spine. They are responsible for modulating pain sensations. CB2 receptors are primarily located in the immune system and they support anti-inflammatory function. The body naturally produces endocannabinoids which bind to these receptors to help establish stability where needed. Cannabinoids, such as THC and CBD, perform a similar function. As such, scientists believe cannabinoids can play an important role in regulating the endocannabinoid system and maintaining stability in the body.

Endocannabnoid System

Related Posts

New Adult-Use Guidelines

Loyalty Program FAQ

Welcome to Grow West!


