The more you know about the plant and its healing properties the easier it is to find the right product for you.
Cannabis Glossary
What are Terpenes
Terpenes are volatile organic compounds produced by most plants, as well as some small animals and insects. They are responsible for the pungent aromas emitted by cannabis. In nature, terpenes protect plants from environmental stressors.
There are over 200 terpenes that can be found in cannabis, but a select few are particularly common. Each terpene has a distinctive aroma and unique set of medicinal benefits. In some cases, terpenes interact with cannabinoids, or each other, to enhance medicinal benefits. This is called the entourage effect.
The types

Pinene has a piney, herbal aroma. It is also found in pine trees, turpentine, dill, parsley, and basil. Note: High levels of myrcene found alongside pinene may offset feelings of clarity.

Myrcene has an earthy, musky aroma. One of the most commonly found terpenes in cannabis, but can also be found in mangoes, lemongrass, basil, and thyme.

Limonene has a sweet, citrus aroma. It is also found in citrus fruits, mint, juniper, and rosemary. It can help improve the absorption of other terpenes.

Ocimene has a woodsy, mint aroma. Also found in mint, parsley, pepper, and basil, it is known to contain a wealth of regularly useful medicinal properties.

Terpinolene has a floral, herbal aroma. It is also found in nutmeg, tea tree, conifers, apples, cumin, and lilacs.

Linalool has a sharp floral aroma. It is also found in lavender and coriander.

Caryophyllene has a spicy, peppery aroma. It is also found in black pepper, cloves, cinnamon, oregano, basil, hops, and rosemary.

Humulene has a sharp earthy aroma. It is also found in hops, clove, and basil.

trans-Nerolidol has a floral, citrus aroma. It is also found in jasmine, tea tree, and lemongrass.

Sources: The Medical Marijuana Dispensary by Laurie Wolf and Mary Wolf and Leafly.com
Cannabis Use Guidelines
Different products like flower, edibles, and concentrates require different tools, have varying effects, and require specific precautions. Flower provides immediate effects via vaporization or smoking and can last up to 3 hours. Edibles are more powerful and last for longer periods of time, so start at low doses and gradually increase after allowing up to 6 hours to feel the results. Concentrates are highly potent in small quantities.
First time cannabis use
Ensure that your first time consuming cannabis is a positive experience
Impaired Driving
Busting the driving high myth
Be Mindful with Concentrates
Microdosing
Consuming small amounts of cannabis to enjoy the benefits without the potential negative side effects
Cannabis for Seniors
Seniors are the fastest growing population of new medical cannabis users, yet many senior citizens remain misinformed about cannabis. This age demographic may even reap the most benefit from this medicinal plant. Most seniors take prescription drugs on a daily basis. The side effects of cannabis are insignificant compared to those of some prescription drugs. Furthermore, the powerful anti-oxidant effects of cannabis can provide relief for many medical conditions.
Ask your provider how cannabis may help your conditions(s). Medical cannabis could become a valuable tool in your “wellness toolbox”.
Cannabis for Seniors
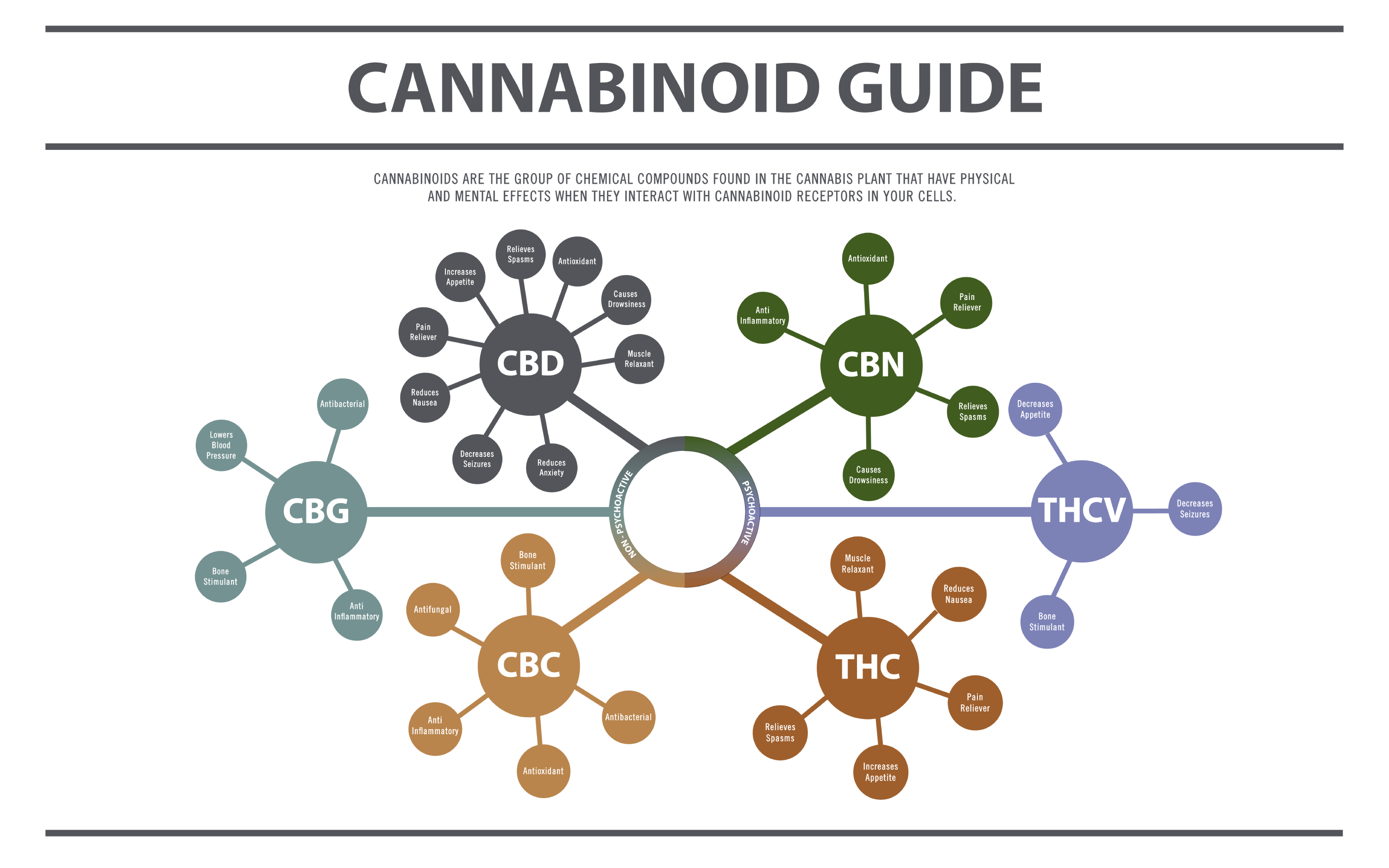
What is in Cannabis?
Cannabis is made up of cannabinoids, terpenes, and to a lesser degree, flavonoids. Cannabinoids are chemical compounds that make up the majority of a strain. Each contains a unique set of properties. CBD and THC are the two most common and frequently sought-after cannabinoids. Others, such as CBC and CBN, are less common, but they do affect the quality of your medicine. This also applies to the many terpenes in the cannabis plant.
More on cannabinoids:
CBD – Cannabidiol is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid. It contains anticonvulsant, analgesic, antinausea, anti-inflammatory, and anti-anxiety properties. It is most commonly found in hemp and high-CBD cannabis cultivars.
CBN – Cannabinol is a lightly psychoactive cannabinoid known for its sedative properties. It is relatively uncommon in flower and often used in processed cannabis products. It contains anticonvulsant, antidepressant, and analgesic properties. It can also help reduce muscle spasms and intraocular pressure.
THC – Tetrahydrocannabinol is the primary psychoactive cannabinoid found in cannabis. It is known to help alleviate a number of ailments, including pain, inflammation, insomnia, nausea, depression, and anxiety.
CBG – Cannabigerol is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid known to help treat glaucoma by reducing intraocular pressure. It also contains anti-oxidant, antifungal, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory properties.
THCV – Tetrahydrocannabivarin is a psychoactive cannabinoid known for its appetite suppressant properties. It has potential to help treat osteoporosis and contains anti-anxiety and anti-inflammatory properties.
CBC – Cannabichromene is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid. It contains analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and antifungal properties. Research suggests that it may help regenerate brain cells and may help treat fibromyalgia, multiple sclerosis, dementia, and Alzheimer’s disease.
Sources: The Medical Marijuana Dispensary by Laurie Wolf and Mary Wolf and apothecarium.com
Cannabis Basics 101
An Introduction to CBD
Cannabis and Pain Management
Chronic pain affects up to 38 million Americans and is a typical reason cited for medical cannabis use. Research has shown that cannabis may be helpful with pain management especially if paired with mild physical exercise like yoga.
Pain Management
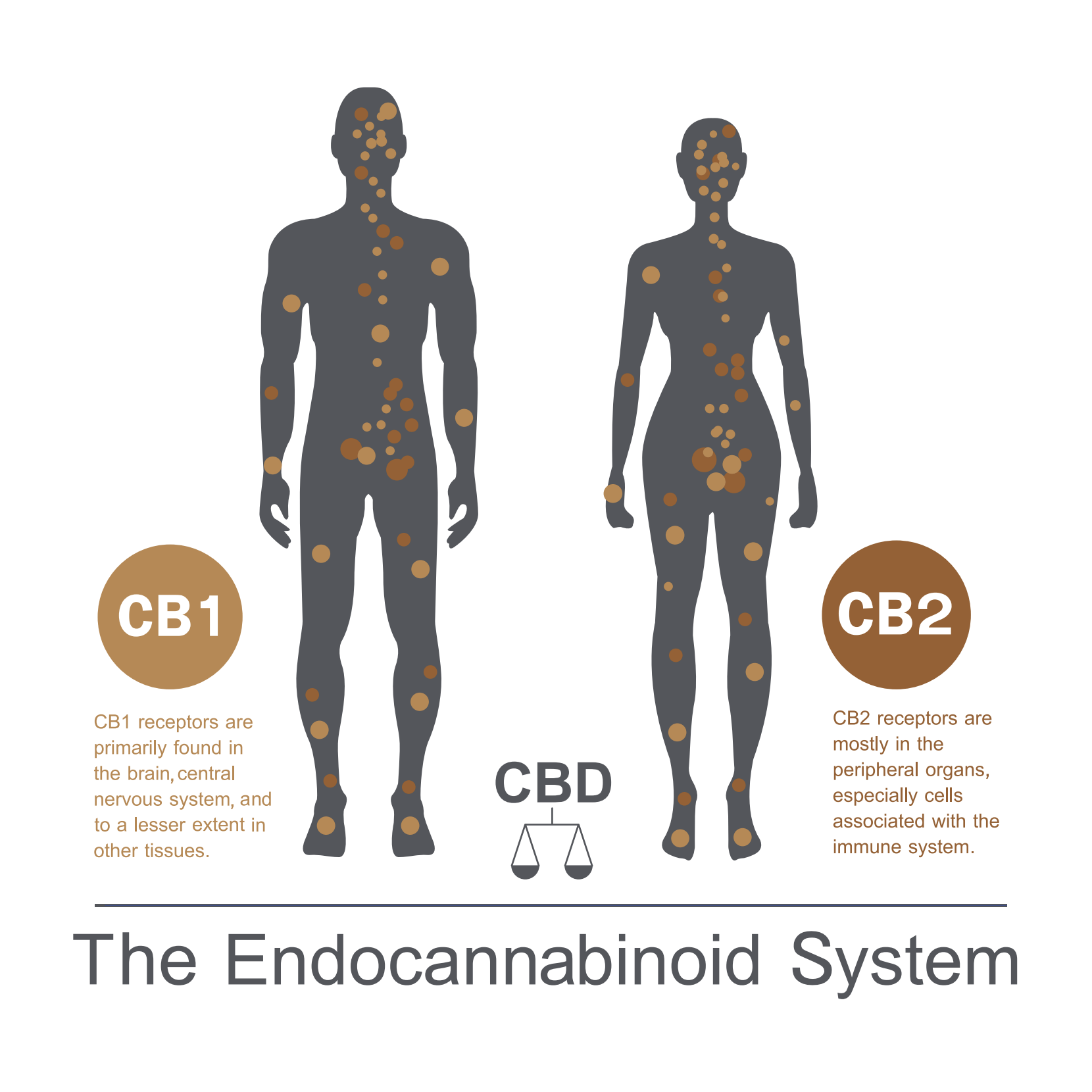
How does Cannabis work?
The human body is equipped with an endocannabinoid system (ECS), a series of cellular receptors that react to imbalances within the body and work to establish stability, or homeostasis. The system consists of two receptors, CB1 and CB2. CB1 receptors are primarily located in the brain, central nervous system, and spine. They are responsible for modulating pain sensations. CB2 receptors are primarily located in the immune system and they support anti-inflammatory function. The body naturally produces endocannabinoids which bind to these receptors to help establish stability where needed. Cannabinoids, such as THC and CBD, perform a similar function. As such, scientists believe cannabinoids can play an important role in regulating the endocannabinoid system and maintaining stability in the body.
Endocannabinoid System
Opioids and Cannabis
There has been a significant increase in opioid related deaths in recent years. Cannabis has been proven to be less addictive and have fewer side effects than opioids. Patients can complement their prescriptions with medical cannabis to avoid overdose.

